Along with the advancement of technology, improvement of living standards, and the development of the mechanical industry, traditional welding technology cannot catch up with the requirement of the fast-developing society. The more widely used automatic welding technology improves production, reduces costs, and increases working efficiency. Here we’ll further discuss the developing trend of automatic welding by deep learning the advantages and the principle of automatic welding.
Keywords: automatic welding, application, robotic welding
The importance of automatic welding technology
With the development of modern technology and digital electronic system, automation is getting closer and closer to our lives. The progress of automatic welding technology endows the welding industry with new vitality. The popularization of welding automation is of great significance to increase production efficiency, to conserve energy, and reduce emissions. Therefore, researching the reasonable and efficient application of automatic welding technology in machining have much more significance.

What is automatic welding?
Automatic welding is a complete mechanized and automated process of the whole welding process. The traditional welding refers to manual welding.
‘In manual metal arc welding, the arc is struck between a consumable electrode and the workpiece being welded. The electrode rod is melted at the tip of the arc and metal droplets fall into the weld pool. Thus, as welding progresses the welding electrode becomes shorter. The welder must maintain a constant arc length between the workpiece and the tip of the electrode as the electrode moves along the joint seam while compensating for the burn-off rate of the electrode.’ –Sciencedirect
Automatic welding is different. The welding process is completed mechanized by modern electronic and digital technology. Automatic welding includes semiautomatic and fully automatic. In semiautomatic welding, an operator manually loads the parts into the welding fixture. A welder controller then keeps the welding process, the motion of the torch, and stillness of the parts to preset parameters. After the weld is completed, the operator removes the completed assembly and the process begins again. In fully automatic welding, it doesn’t require a manual welder to perform them, but instead, an operator controls the machine or robot which carries out the welds. A custom machine, or series of machines, loads the workpiece, indexes the part or torch into position, accomplishes the weld, monitors the quality of the joint and unloads the finished product.
Here are the most basic components of an automated welding system, all of which are important to the automated welding process:
Wire Feeder: This moves filler wire into the robot at a programmed rate. This filler wire is often used to add material to a weld to support the joint.
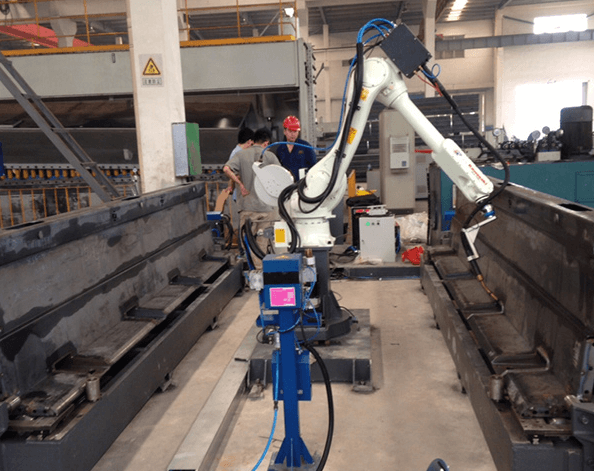
Welding Robot: This includes the robot and the tool at the end of the arm, typically a torch or other manipulator. These robots come in two types: articulating robots and rectilinear robots. Rectilinear robots can move their primary arm in three directions and rotate a wrist at the end of the arm. Articulating robots have rotating joints — these allow for more freedom of movement and range of motion outside of three dimensions.
Wire Cleaner: The cleaner is used to remove spatter from the torch between work cycles, prolonging equipment life span.
Torch: The torch uses power flowing to an electrode to heat up and join metals together. Arc welding units also have an arc shielding apparatus included in the torch. Also, an air- or water-cooling unit is usually included.
Work Area: This is where parts are placed and held for the robot to weld. Fixtures hold the parts in place as the robot completes its welds.
Controller: This component is effectively the “brain” of the welding cell, supplying power and instructions to the robot using stored programs.
Teach Pendant: This handheld interface system allows the operator to set welding parameters, manually move the robot and input new programs.
Welding Power Supply: This supplies power to the welding torch. This will vary in size and performance depending on the requirements of the parts being welded. The power supply differs slightly depending on whether the cell is an arc welding unit or a spot-welding unit.
Stack Light: This light indicates what the cell is doing at any given time. Generally, a red light indicates an emergency stop, an orange light means the robot is being programmed and green means the cell is running automatically.
Operation Box: This box contains controls to start and stop a cell, and it contains buttons for each function, including a restart button to reset the cell after a malfunction has been resolved.
Safety Features: Most robotic welding machines will include safety features to prevent harm to workers and operators. These include fencing, arc shielding, access doors, and other features to reduce worker exposure to hazardous light, fumes and motion as a cell works.
The advantages of automated welding
Automated welding systems offer four main advantages: increased productivity, improved weld quality, decreased scrap, decreased variable labor costs and improved the operating environment more easily.
1, improved the productivity
A mechanized welding system can easily outpace a skilled manual welder. The production weld speeds of automated welding are set at a max percentage by the machine, not by an operator. Automated welding systems can run 24/7 without a break. Automated welding is faster than doing it manually and certainly more consistent, which simplifies production planning and management because a stable cycle time leads to predictable output per hour, shift and day.
2, improved quality
Automated welding systems ensure weld integrity through electronic weld process controllers. Combining mechanized torch and part motions with the electronic recall of welding parameters result in a higher quality weld than can be accomplished manually. The consistent motion also means consistent quality. With the torch and workpiece(s) in the same position and moving at the same speed every time, each part is welded the same way. There's no risk of variation, and as the robot never tires, the last piece produced is identical to the first. Especially for safety-critical parts, automation gives customers confidence in the integrity of each weld.
3, save costs
Shorter cycle times and longer working hours add up to a lower cost per weld, but that's not the only cost savings. Automated welding cuts both scrap and consumable costs.
Decreased scrap: Human error is always possible, even with the most skilled welders. However, every movement a welding robot makes is planned and automated, reducing mistakes and, therefore, reducing the number of scrapped parts.
Decrease wastes: Consumables are yet another source of waste. Consumables include nozzles and other components with relatively short life spans that are replaced after a certain number of uses. Robotic welding units increase welding speed and minimize excess energy use, increasing the lifespan of each consumable component. This means new consumables are purchased less frequently, saving costs.
4, save energy
Automated welding systems conserve energy by running consistently, cutting the energy-expensive start-ups. Additionally, robots do not over the weld and reduce the need for corrective welding, cutting energy expenditure.
5, safer working conditions
Welders need protection against the arc flash and the weld’s heat. Automated welding keeps workers away from these hazards and creates a safer, more pleasant working environment. Plus, there’s no need to invest in additional personal protective equipment.
When using Automatic welding is most commonly used in the manufacturing and engineering industries to increase efficiency. The typical models of automatic welding technology used in mechanical welding are mechanical arm and welding robot. Programs are input via the teach pendant and saved to the controller, which tells the robot what to do. These programs move the welding robot and manipulate the torch on the end of its arm, placing it exactly where it needs to be at any point. The torch heats up, using a power supply to generate enough heat in the metal to fuse parts permanently. The wire feeder feeds extra material to the robot arm to do this. Between parts, the arm moves the torch to the wire cleaner to remove any spatter.
Instead of choosing a robotic welding setup manufacture, you can choose a contract manufacturer with welding robots for OEM. As a professional metal fabrication manufacturer, Openex possesses various welding machines and has skilled welders certified by AWS, CSS, RINA, LR, DNB, API as well as ASME. We are experienced in the following welding process: Arc Welding, MIG Welding, TIG Welding, Shielded Metal Arc Welding, MAG Welding, Plasma Arc Welding, and so on. Custom welding services from the professional welders at Openex are sure you get the results you are looking for in product manufacturing and custom fabrication.
If you need complete custom fabrication or just simple welding fabrication services, contact us right the time.
Link to this article:Automated welding and its advantages
Reprint Statement: If there are no special instructions, all articles on this site are original. Please indicate the source for reprinting.:Casting Wiki,THANKS!^^